- Google Cloud
- Articles & Information
- Cloud Product Articles
- Distance Matrix API from Google Maps Platform in A...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Article History
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Google Maps Platform features now available to ABAP developers in the latest release of ABAP SDK for Google Cloud V1.5
To know more about what’s new with ABAP SDK for Google Cloud V1.5 check out this link: ABAP SDK for Google Cloud V1.5
In this blog, we will explore what are the Google Maps Platform APIs and how we can consume them in ABAP using an example for the Distance Matrix API:
Google Maps Platform is a suite of APIs and services that allows developers to add maps and location functionality to their applications. This is a great opportunity for ABAP developers to create innovative applications right from the platform they are familiar with. This means that ABAP developers can now create applications that include maps, directions, and other location functionality.
With the ABAP SDK for Google Cloud, ABAP developers can now create applications that take advantage of the power and flexibility of Google Maps Platform services. The ABAP SDK for Google Cloud now includes APIs for a variety of Google Maps Platform features, including:
Address validation: Validate addresses to ensure that they are accurate and complete. This can be useful for applications that need to collect user addresses, such as e-commerce applications and shipping applications.
Directions: Get directions between two locations, including driving, biking, and walking directions. This can be useful for applications that need to provide users with directions, such as navigation applications and travel applications.
Distance Matrix: Calculate the distance between multiple locations. This can be useful for applications that need to calculate shipping costs or delivery times.
Elevation: Get the elevation of a location. This can be useful for applications that need to calculate the slope of a terrain or to determine the visibility from a given location.
Geocoding: Convert addresses into geographic coordinates (latitude and longitude), and vice versa. This can be useful for applications that need to place markers on a map or find nearby places.
Places: Search for and discover places, such as restaurants, shops, and attractions. This can be useful for applications that need to provide users with information about local businesses and attractions.
Roads: Get information about roads, such as traffic conditions and speed limits. This can be useful for applications that need to provide users with traffic updates or to calculate travel times.
Time Zones: Get the time zone of a location. This can be useful for applications that need to display the correct time for users in different locations.
The Distance Matrix API is one of the most popular and useful Google Maps Platform APIs. Let’s explore it in more detail.
Distance Matrix API
The Distance Matrix API is a service that accepts an HTTPS request containing origins and destinations for a given mode of transport. For each combination of origin and destination, it returns travel distance and duration.
You can use the Distance Matrix API to help determine the most efficient travel routes between multiple possible origins and destinations. For example, which workers to send to job sites, or from which warehouses to send packages.
What can the API do?
With the Distance Matrix API, you can provide travel distance and time for a matrix of origins and destinations. You can specify several options, including mode of transportation, such as driving, biking, transit or walking, as well as transit modes, such as bus, subway, train, tram, or rail.
The Distance Matrix API provides information based on the recommended route between start and end points. You can request these kinds of distance data:
Distance for a selected travel mode
Distance in kilometre or miles
Estimated travel time in traffic
How does the API Work?
The Distance Matrix API uses any number of origins (starting points) and destinations, and returns the distance and travel time between each origin and all requested destinations, starting with the first origin in the request and proceeding step-wise to the next.
For example, if your request specifies A and B as origins, and C and D as destinations, it returns distances and travel time in this order:
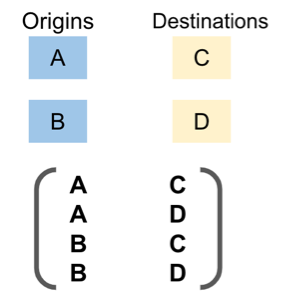
Like a matrix, therefore the name Distance Matrix
Applications of Distance Matrix API to enrich SAP Business Process
Logistics and Transportation:
The Distance Matrix API can be used to calculate accurate distances and travel times between multiple origins and destinations. This information can be used to optimise route planning, improve delivery times, and reduce transportation costs. For example, in logistics this API could be used to determine the most efficient route for a fleet of delivery vehicles
Customer Service:
The Distance Matrix API can be used to provide customers with accurate estimates of travel time or delivery times. This information can be used to improve customer satisfaction and reduce the number of customer inquiries. For example, a company could use the API to provide customers with an estimated delivery time of an order.
Field Service:
The Distance Matrix API can be used to optimize the scheduling of field service technicians. By knowing the distances and travel times between customer locations, companies can ensure that technicians are assigned to the most efficient routes. For example, a company could use the API to determine which technician is closest to a customer location
Analogy to Google Maps App — Real World Scenario
Almost everyone who uses a smartphone has used Google Maps to look up distance and travel time information at some point, whether it’s on their computer or on their phone.
Below screenshot is a quick snapshot of distance between two offices in the Bengaluru City (Karnataka, India):
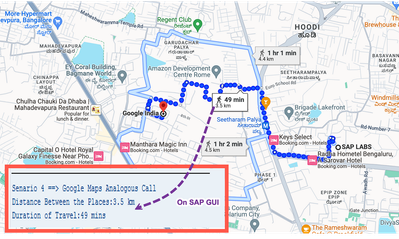
You will see how this can be similarly achieved in Scenario 4 in the blog below.
Let’s take a look at how to use the Distance Matrix API provided by the ABAP SDK for Google Cloud.
Let’s get coding!
Before you begin
Before you start writing code to consume the API, make sure that you or your administrators have completed the following prerequisites:
- You have a Google Cloud account and project. Please keep the Project Id with you which is available in Google Cloud Dashboard
- Billing is enabled for your project. See how to confirm that billing is enabled for your project.
- Configure a client key for authentication. To set up this client key, please follow the instructions provided in the Secret Manager Blog
In your Google Cloud Console, Navigate to Google Maps Platform and enable the Distance Matrix API. You would see a tile as shown below(the API has been enabled in this case).
Once the required Client Key configuration is successfully done and validated we can use the Distance Matrix API with the API key that is stored in Secret Manager.
Here are some code examples of how to use the Distance Matrix API provided by the ABAP SDK for Google Cloud:
1. Distance and Travel Time Between Two Places:
Distance Matrix API can give Distance and Travel Time information between one origin and one destination
"Data declarations
DATA:
lt_destinations TYPE /goog/cl_distance_matrix=>ty_t_string,
lt_origins TYPE /goog/cl_distance_matrix=>ty_t_string,
lv_departure_time TYPE /goog/num_float,
ls_output TYPE /goog/if_maps=>ty_014.
TRY.
"Instantiate the client stub
DATA(lo_dist_matrix) = NEW /goog/cl_distance_matrix( iv_key_name = 'TEST-DISTANCE_MATRIX' ).
WRITE:/ |Scenario 1 ==> Single origin and single destination|.
lt_origins = VALUE #( ( |NewYork City, NY| ) ).
lt_destinations = VALUE #( ( |Washington DC| ) ).
"Call the API method
CALL METHOD lo_dist_matrix->distance_matrix
EXPORTING
it_q_destinations = lt_destinations
it_q_origins = lt_origins
IMPORTING
es_output = ls_output
ev_ret_code = DATA(lv_ret_code)
ev_err_text = DATA(lv_err_text)
es_err_resp = DATA(ls_err_resp).
IF lo_dist_matrix->is_success( lv_ret_code ).
IF lo_dist_matrix->is_status_ok( ).
TRY.
WRITE:/ |Distance Between the Places:| && ls_output-rows[ 1 ]-elements[ 1 ]-distance-text.
WRITE:/ |Estimated Duration of Travel:| && ls_output-rows[ 1 ]-elements[ 1 ]-duration-text.
CATCH cx_sy_itab_line_not_found.
WRITE:/ |Distance & Time Could not be Found|.
ENDTRY.
ELSE.
WRITE: ls_output-status && ls_output-error_message.
ENDIF.
ELSE.
WRITE:/ |Error encountered| && lv_err_text.
ENDIF.
CATCH /goog/cx_sdk INTO DATA(lo_exception).
"Display exception message
MESSAGE lo_exception->get_text( ) TYPE 'E'.
ENDTRY.2. Distance and Travel Time Between Multiple Origins and Destination
"Data declarations
DATA:
lt_destinations TYPE /goog/cl_distance_matrix=>ty_t_string,
lt_origins TYPE /goog/cl_distance_matrix=>ty_t_string,
lv_departure_time TYPE /goog/num_float,
ls_output TYPE /goog/if_maps=>ty_014.
TRY.
"Instantiate the client stub
DATA(lo_dist_matrix) = NEW /goog/cl_distance_matrix( iv_key_name = 'TEST-DISTANCE_MATRIX' ).
WRITE:/ |-------------------------------------------------------|.
WRITE:/ |Senario 2 ==> Multiple origin and multiple destinations|.
lt_origins = VALUE #( ( |San Francisco| )
( |Victoria BC| ) ).
lt_destinations = VALUE #( ( |Vancouver BC| )
( |Seattle| ) ).
"Call the API method
CALL METHOD lo_dist_matrix->distance_matrix
EXPORTING
it_q_destinations = lt_destinations
it_q_origins = lt_origins
IMPORTING
es_output = ls_output
ev_ret_code = lv_ret_code
ev_err_text = lv_err_text
es_err_resp = ls_err_resp.
IF lo_dist_matrix->is_success( lv_ret_code ).
IF lo_dist_matrix->is_status_ok( ).
TRY.
WRITE:/ |Distance Between the San Franciso & Vancouver BC:| && ls_output-rows[ 1 ]-elements[ 1 ]-distance-text.
WRITE:/ |Distance Between San Franciso & Seattle:| && ls_output-rows[ 1 ]-elements[ 2 ]-distance-text.
WRITE:/ |Distance Between Vancouver BC & Victoria BC:| && ls_output-rows[ 2 ]-elements[ 1 ]-distance-text.
WRITE:/ |Distance Between Vancouver BC & Seattle:| && ls_output-rows[ 2 ]-elements[ 2 ]-distance-text.
CATCH cx_sy_itab_line_not_found.
WRITE:/ |Error in retrieving data|.
ENDTRY.
ELSE.
WRITE: ls_output-status && ls_output-error_message.
ENDIF.
ELSE.
WRITE:/ |Error encountered| && lv_err_text.
ENDIF.
CATCH /goog/cx_sdk INTO DATA(lo_exception).
"Display exception message
MESSAGE lo_exception->get_text( ) TYPE 'E'.
ENDTRY.3. Distance and Travel Time Between Two Places with preferred travel modes and stipulated departure time
Distance Matrix API can give Distance and Travel Time information based on travel and transit mode along with a provided departure time.
Please note: departure time cannot be in the past.
In this example we show the travel mode driving is used along with transit mode bus
"Data declarations
DATA:
lt_destinations TYPE /goog/cl_distance_matrix=>ty_t_string,
lt_origins TYPE /goog/cl_distance_matrix=>ty_t_string,
lv_departure_time TYPE /goog/num_float,
ls_output TYPE /goog/if_maps=>ty_014.
TRY.
"Instantiate the client stub
DATA(lo_dist_matrix) = NEW /goog/cl_distance_matrix( iv_key_name = 'TEST-DISTANCE_MATRIX' ).
WRITE:/ |-------------------------------------------------------|.
WRITE:/ |Senario 3 ==> Call with preferred modes and stipulated departure time|.
lt_origins = VALUE #( ( |NewYork City, NY| ) ).
lt_destinations = VALUE #( ( |Washington DC| ) ).
cl_pco_utility=>convert_abap_timestamp_to_java(
EXPORTING
iv_date = sy-datum
iv_time = sy-uzeit
IMPORTING
ev_timestamp = lv_departure_time
).
"Convert millisecond to seconds
lv_departure_time = lv_departure_time / 1000.
"Call the API method
CALL METHOD lo_dist_matrix->distance_matrix
EXPORTING
it_q_destinations = lt_destinations
it_q_origins = lt_origins
iv_q_departure_time = lv_departure_time
iv_q_mode = 'driving'
iv_q_traffic_model = 'best_guess'
iv_q_transit_mode = 'bus'
IMPORTING
es_output = ls_output
ev_ret_code = lv_ret_code
ev_err_text = lv_err_text
es_err_resp = ls_err_resp.
IF lo_dist_matrix->is_success( lv_ret_code ).
IF lo_dist_matrix->is_status_ok( ).
TRY.
WRITE:/ |Distance Between the Places:| && ls_output-rows[ 1 ]-elements[ 1 ]-distance-text.
WRITE:/ |Duration of Travel:| && ls_output-rows[ 1 ]-elements[ 1 ]-duration-text.
WRITE:/ |Duration in Traffic:| && ls_output-rows[ 1 ]-elements[ 1 ]-duration_in_traffic-text.
CATCH cx_sy_itab_line_not_found.
WRITE:/ |Error in retrieving data|.
ENDTRY.
ELSE.
WRITE: ls_output-status && ls_output-error_message.
ENDIF.
ELSE.
WRITE:/ |Error encountered| && lv_err_text.
ENDIF.
CATCH /goog/cx_sdk INTO DATA(lo_exception).
"Display exception message
MESSAGE lo_exception->get_text( ) TYPE 'E'.
ENDTRY.4. Travel Time Between Places using different mode of transport
Distance Matrix API can give Distance and Travel Time information based on different travel modes, in this example we use travel mode as walking
"Data declarations
DATA:
lt_destinations TYPE /goog/cl_distance_matrix=>ty_t_string,
lt_origins TYPE /goog/cl_distance_matrix=>ty_t_string,
lv_departure_time TYPE /goog/num_float,
ls_output TYPE /goog/if_maps=>ty_014.
TRY.
"Instantiate the client stub
DATA(lo_dist_matrix) = NEW /goog/cl_distance_matrix( iv_key_name = 'TEST-DISTANCE_MATRIX' ).
WRITE:/ |-------------------------------------------------------|.
WRITE:/ |Senario 4 ==> Google Maps Analogous Call|.
DATA: lv_str TYPE string.
lv_str = |SAP LABS, Whitefield, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India|.
cl_http_utility=>escape_url(
EXPORTING
unescaped = lv_str " Unencoded String
RECEIVING
escaped = lv_str " URL-Encoded String
).
lt_origins = VALUE #( ( lv_str ) ).
lv_str = |Google India, Ferns city, Doddanekkundi, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India|.
cl_http_utility=>escape_url(
EXPORTING
unescaped = lv_str " Unencoded String
RECEIVING
escaped = lv_str " URL-Encoded String
).
lt_destinations = VALUE #( ( lv_str ) ).
cl_pco_utility=>convert_abap_timestamp_to_java(
EXPORTING
iv_date = sy-datum
iv_time = sy-uzeit
IMPORTING
ev_timestamp = lv_departure_time ).
"Convert millisecond to seconds
lv_departure_time = lv_departure_time / 1000.
"Call the API method
CALL METHOD lo_dist_matrix->distance_matrix
EXPORTING
it_q_destinations = lt_destinations
it_q_origins = lt_origins
iv_q_departure_time = lv_departure_time
iv_q_mode = 'walking'
IMPORTING
es_output = ls_output
ev_ret_code = lv_ret_code
ev_err_text = lv_err_text
es_err_resp = ls_err_resp.
IF lo_dist_matrix->is_success( lv_ret_code ).
IF lo_dist_matrix->is_status_ok( ).
TRY.
WRITE:/ |Distance Between the Places:| && ls_output-rows[ 1 ]-elements[ 1 ]-distance-text.
WRITE:/ |Duration of Travel:| && ls_output-rows[ 1 ]-elements[ 1 ]-duration-text.
CATCH cx_sy_itab_line_not_found.
WRITE:/ |Error in retrieving data|.
ENDTRY.
ELSE.
WRITE: ls_output-status && ls_output-error_message.
ENDIF.
ELSE.
WRITE:/ |Error encountered| && lv_err_text.
ENDIF.
CATCH /goog/cx_sdk INTO DATA(lo_exception).
"Display exception message
MESSAGE lo_exception->get_text( ) TYPE 'E'.
ENDTRY.You can access the complete program provided as a quick-start guide in the ABAP SDK for Google Cloud’s GitHub Repo
On successful execution, you can see a program output as below:
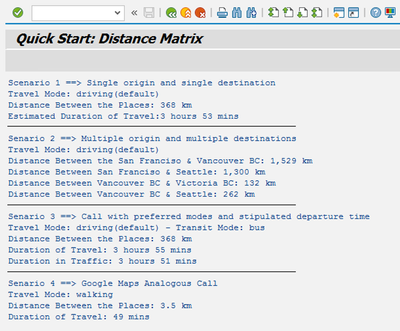
Conclusion
The Distance Matrix API is an useful API that can be used to add geospatial intelligence into your SAP applications. If you are working with location data in SAP, we encourage you to learn more about the Distance Matrix offered as part of the ABAP SDK for Google Cloud.
Next Steps
Hope the article was able to give you a quick insight on using Distance Matrix API with ABAP SDK for Google Cloud.
Ready to start using ABAP SDK for Google Cloud?
Bookmark What’s new with the ABAP SDK for Google Cloud for the latest announcements and follow installation and configuration instructions.
Check out these blog posts to get started with ABAP SDK for Google Cloud
- This blog, explains how you can evaluate ABAP SDK for Google Cloud using ABAP Platform Trial 1909 on Google Cloud Platform.
- Read this blog post to get a sneak peek on how a business process such as Sales Order entry in SAP can be automated using ABAP SDK for Google Cloud.
- This blog is an excellent start to understand how BigQuery ML which is a powerful machine learning service that lets you build and deploy models using SQL queries. you can now be accessed with ABAP SDK for Google Cloud.
- Read this blog post to understand how to use Secret Manager with ABAP SDK.
- Also check out blog post about ABAP SDK Code Wizard, and on Application logging as some of the many Engineering excellence delivered as part of ABAP SDK.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hey, this is my code to access the new distance matrix endpoint:
def get_distance_matrix(origin_addresses, destination_addresses):
URL = "https://routes.googleapis.com/distanceMatrix/v2:computeRouteMatrix"
origins = [
{"waypoint": {"address": address}} for address in to_list(origin_addresses)
]
destinations = [
{"waypoint": {"address": address}} for address in to_list(destination_addresses)
]
data = {"origins": origins,
"destinations": destinations, "travelMode": "DRIVE"}
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"X-Goog-Api-Key": GOOGLE_MAPS_API_KEY,
"X-Goog-FieldMask": "originIndex,destinationIndex,duration,distanceMeters,status,condition",
}
response = requests.post(URL, headers=headers, json=data)
I would like to use the google-maps-routing posting library. I come up with something like:
def get_distance_matrix_google_routing(origin_addresses, destination_addresses):
# Initialize the Routing client
client = routing_v2.RoutesClient()
# Construct origin and destination waypoints
origins = [types.RouteMatrixOrigin(waypoint=types.Waypoint(
address=address)) for address in origin_addresses]
destinations = [types.RouteMatrixDestination(waypoint=types.Waypoint(
address=address)) for address in destination_addresses]
# Construct the request
request = types.ComputeRouteMatrixRequest(
origins=origins,
destinations=destinations,
travel_mode=types.RouteTravelMode.DRIVE,
units=types.Units.IMPERIAL, # Get the results in miles
)
# Set the FieldMask header
# Send the request with the metadata
response = client.compute_route_matrix(request=request)
It is not working because I'm not providing the FieldMask as I do with the first method. Could you help me out? LLMs don't know how to deal well with the new Routing endpoint yet.

 Twitter
Twitter